
Top 15 MCSA Interview Question and Answers
Question 1
How to changing ntds.dit file from one Drive to another?
We are going to see how to do that.
- Boot the domain controller in Directory Services Restore spectre and log on with the Directory Services Restore Mode administrator account and password (this is the password we assigned during the Dcpromo process).
- At a command prompt, type ntdsutil.exe. We receive the following prompt:ntdsutil:
- Type files to receive the following prompt:file maintenance:
- Type info. Note the path of the database and log files.
- To move the database, type move db to %s (where %s is the target folder).
- To move the log files, type move logs to %s (where %s is the target folder).
- Type quit twice to return to the command prompt.
- Reboot the computer normally.
Question 2
Explain DNS (Domain Name System).
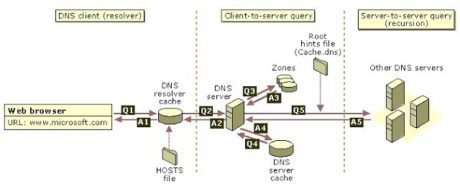
The local DNS resolver
The following graphic explains an overview of the complete DNS query process.
Question 3
What are the different Zones in DNS?
Reverse lookup zone – IP address to name map.
Primary Zones – It contains Read and Write copies of all resource records (A, NS, _SRV).
Secondary Zones – It holds read-only copies of the Primary Zones.
Stub Zones
Ideally, stub zones are like secondary zones in that they contain a read-only replica of a primary zone. Stub zones are more effective and generate less copying traffic.
Stub Zones just have 3 records, the SOA for the primary zone, NS record and a Host (A) record. The notion is that if a client queries a record in the Stub Zone, your DNS server can refer that query to the exact Name Server because it knows its Host (A) record.
Question 4
What are the types of Queries?
Inverse – Receiving the name from the IP address. These are used by servers as a security check.
Iterative – Server gives its best answer. This type of inquiry is sent from one server to another.
Recursive – Cannot indicate the query to another name server.
Question 5
What is Conditional Forwarding?
Question 6
Describe the purpose of Resource Records?
Without resource records, DNS could not do with queries. The aim of a DNS Query is to identify a server that is Authoritative for a particular domain. The easy part is for the Authoritative server to verify the name in the query against its resource records.
Question 7
What are the different types of record?
Every zone has one SOA record that finds out which DNS server is the ruler for domains and subdomains in the zone.
NS (name server) record:
An NS record has the FQDN and IP address of a DNS server authoritative for the zone. Each basically and secondary name server authoritative in the domain should have an NS record.
An (address) record:
By far the very common type of resource record, an A record is used to rectify the FQDN of a particular host into its relevant IP address.
CNAME (canonical name) record:
A CNAME record contains an alias (alternate name) for a host.
PTR (pointer) record is the opponent of an A record, a PTR record is used to resolve the IP address of a host into its FQDN.
SRV (service) record is an SRV record is used by DNS clients to identify a server that is running a peculiar service—for instance, to figure out a domain controller so we can log on to the network. SRV records are key to the operation of Active Directory.
MX (mail exchange) record is an MX record points to one or more computers that process SMTP mail for a company or site.
Question 8
Where DNS resource records will be stored?
After running DCPROMO, A text file including the exact DNS resource records for the domain controller is generated. The file called Netlogon.dns is created in the %systemroot%\System32\config folder and contains all the records needed to register the resource records of the domain controller. Netlogon.dns is used by the Windows 2000 NetLogon service and to support Active Directory for non-Windows 2000 DNS servers.
Question 9
What are the Procedures for changing a Server’s IP Address?
- Alter the Server’s IP address
- Stop the NETLOGON service.
- Rename or delete SYSTEM32\CONFIG\NETLOGON.DNS and NETLOGON.DNB
- Restart the NETLOGON service and run “ipconfig /registerDNS”
- We have to go to one of the other DCs and rectify that its DNS is now pointing to the new IP address of the server. If not, alter the records manually and give it 15 minutes to copy the DNS changes out.
- Run REPLMON and make sure that replication is working live. We may have to wait a little time for things to work out.
Question 10
What do you think the issue may be in the case of the server not displaying the copying of its partner?
- Check to see that the servers can poke each other.
- we need to make sure that both the DNS entries servers for each other point to the proper IP addresses.
- If server A says it copied well that is great, but server B mentions it could not contact Server A, check the DNS setup on Server B. Chances are it has a record for Server A pointing to the wrong place.
- Run Netdiag and see if it explains any errors or issues.
Question 11
What is a Trust Relationship and explain its types?
Two-way trust – When two domains guide access to users on the other domain.
Trusting domain – The domain that permits access to users on another domain.
Trusted domain – The domain that is trusted, whose users have access to the trusting domain.
Transitive trust – A trust which can go beyond two domains to other managed domains in the tree.
Intransitive trust – A single way trust that does not extend beyond two domains.
Explicit trust – A trust that an administrator generates. It is not transitive and is just one way only.
Cross-link trust – An open trust between domains in various trees or in the same tree when a descendant/ancestor relationship does not exist between the two domains.
Forest trust – When two forests have a functional level of Windows 2003, you can use a forest trust to join the forests at the root.
Shortcut trust – When domains that validate users are logically distant from one another, the process of logging on to the network can take a much longer time. We can manually add a shortcut trust between two domains in the same forest to accelerate authentication. Shortcut trusts are transitive and can either be one way or two way.
Windows 2000 just supports the following types of trusts:
Two-way transitive trusts
One way non-transitive trusts.
Question 12
What are the types of Backups?
Copy – Saves files and folders without clearing the archive bit.
Incremental – Incremental backup stores all files that have altered since the last Full,Differential or Incremental backup. The archive bit is cleared.
Differential – A differential backup has all files that have been altered since the last FULL backup. The archive bit is not cleared.
Daily – Saves files and folders that have been modified that day. The archive bit is not cleared.
Question 13
What is Multiplexing?
Question 14
What is Multi-streaming?
To perform a backup, select “Start”, “Programs”, “Accessories”, “System Tools”, and “Backup”. The Windows 2000 “Backup Utility” will start. It contains these tabs:
System data
- The registry
- System start-up files
- Component services data class registration database
- Active Directory (Windows 2000 & 2003 Servers only)
- Certificate server database (Windows 2000 & 2003Servers only)
- SYSVOL folder (Windows 2000 & 2003 Servers only)
Question 15
What are authoritative and non-authoritative restores?
Here at this stage changes are accepted from other domain controllers after the backup is done.
But when we are restoring a domain controller by using backup and restore programs, the standard mode for the restoration is non-authoritative. This connotes the fact that the restored server is brought up-to-date with its copies through the normal replication workings.
Authoritative Active Directory restores: Now modifications are not at all accepted from other domain controllers after the backup is done.
Authoritative restore permits the administrator to retrieve a domain controller, put it back to a particular point in time, and mark objects in Active Directory as being authoritative with respect to their copy partners. Authoritative restore has the capability to increase the version number of the features of all objects in the whole directory. You can authoritatively restore only objects from the configuration and domain-naming contexts. Authoritative restores of schema-naming contexts are not synched. To do an authoritative restoration, we must begin the domain controller in Directory Services Restore Mode.
Also, Read Related Interview Question and Answers as follows:




